Abstract
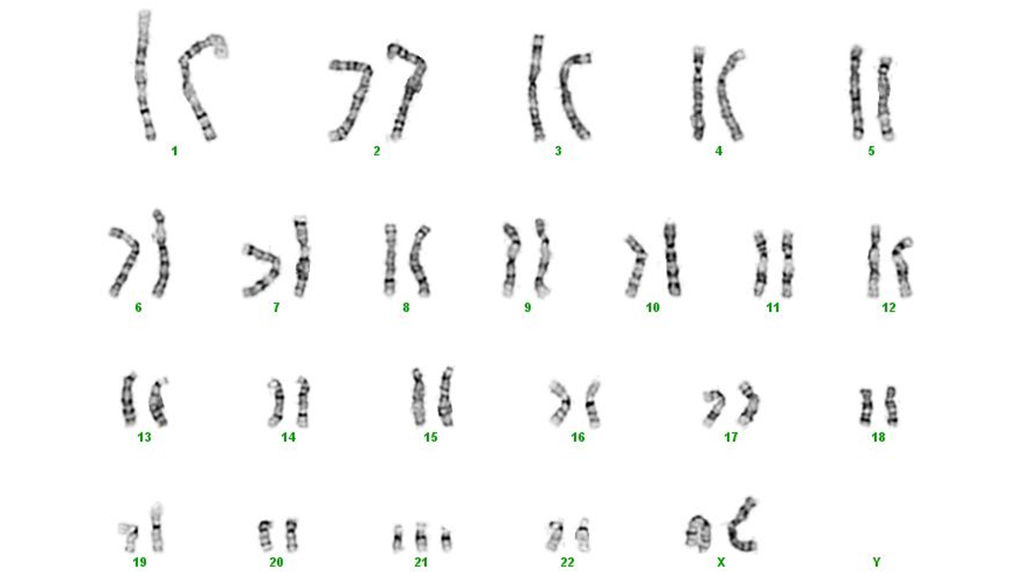
This "clicker case" presents a fictionalized story about a couple ("John" and "Jane") whose new baby is born with Down syndrome; the parents are suing the prenatal clinic where Jane received her care, blaming the clinic for the baby’s condition. Designed for an introductory biology course, the case has students assume the role of an expert witness hired by a law firm to give evidence in the case. To help determine the cause of "Baby Doe’s" condition and whether anyone can be held responsible for it, students need to help the jury understand the process of cell division. In particular, they must explain the behavior of the chromosomes during cell division and how errors in this process can result in conditions such as Down syndrome. The case is presented in class using PowerPoint slides (~1.8 MB) that are punctuated by multiple-choice questions the students respond to using hand-held personal response systems (clickers). It could be adapted for use without these technologies.