Abstract
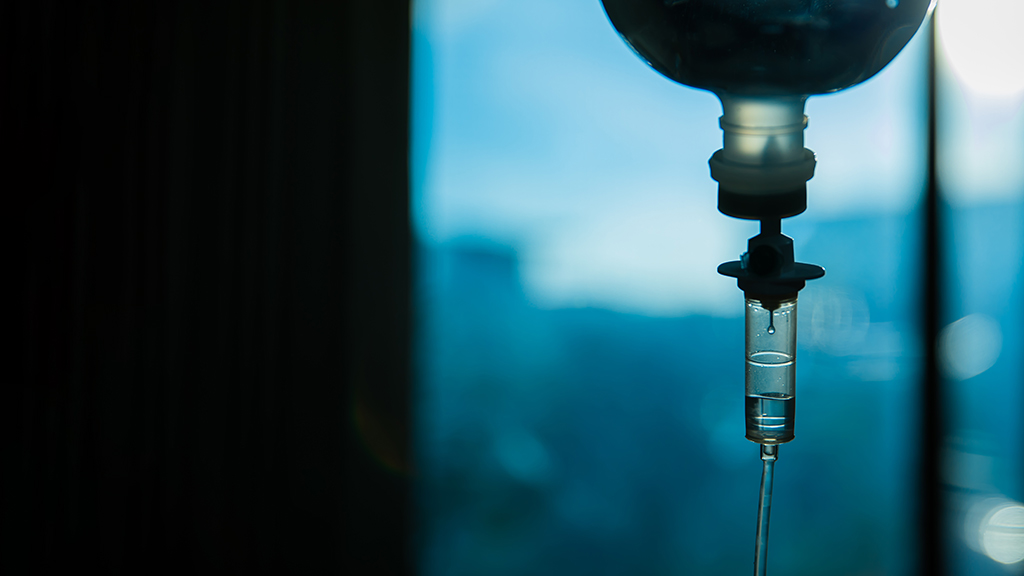
In this directed case study, students are presented with a legal case about a patient who died after an infusion containing the solid precipitate calcium phosphate. The lawsuit was filed to determine if the pharmacist, physician, or nurse was at fault. Students learn about intravenous (IV) infusion incompatibility while reviewing ionic compound naming rules and solubility rules. They also learn how to balance precipitation (double displacement) reactions and analyze laboratory results for electrolyte deficiencies. Finally, students are asked to assign responsibility for the fatality and to suggest a method to prevent the precipitate from forming. The case was written for a first semester general, organic, and biological (GOB) chemistry audience, but it would also be appropriate for high school and undergraduate general chemistry.