Going Wild with the Go Wireless Temp Sensor
By Martin Horejsi
Posted on 2014-03-26
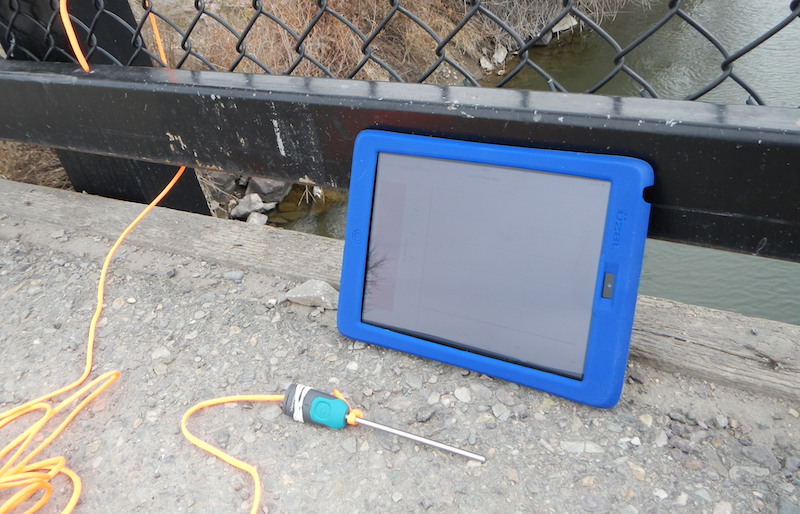
The new Go Wireless Temp sensor is a welcome addition to the suite of Bluetooth tools produced by Vernier that are available for the iPad. While not much larger than the business end of the traditional, wired temperature sensor, the Go Wireless Temp has onboard power and a radio transmitter all nestled in a thumb-sized, water-resistant housing. Although the device’s temperature range is a little narrower on the upper end due to its plastic and electronics, it still safely measures molecular motion from -40°C to 125°C. While the merits of digital temperature probes are well known, and the benefits of wireless peripherals have promoted collaboration and creativity in the science classroom, the Go Wireless Temp has added a new dimension with its light weight, free accompanying app, and 30-meter range. I took the Go Wireless Temp for a spin, looking for ways to leverage the wireless potential of the sensor.
The Go Wireless Temp must be used with a mobile device. To use the sensor with an iPad, you can download either the Go Wireless Temp app, available for free through the iTunes store, or the Vernier’s Graphical Analysis app, available for $4.99, for more powerful data collection and analysis.
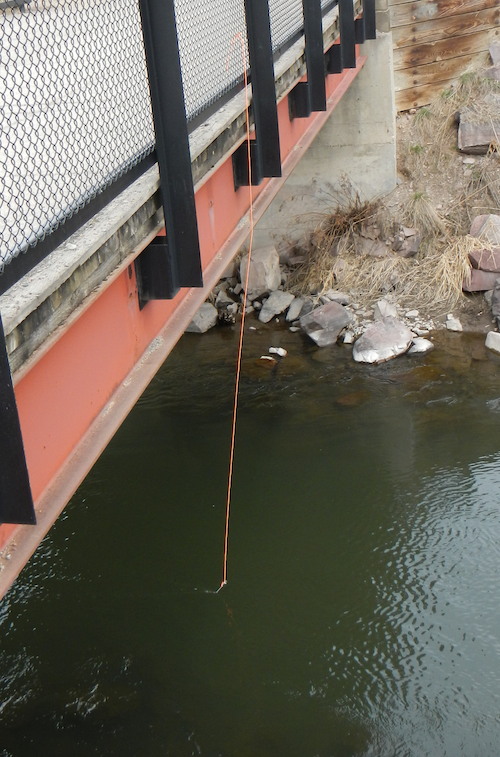
To test the sensor, I attached it to a paracord harness and lowered the sensor off a bridge and into the center of a stream. Once the Go Wireless Temp was tied to a railing, the iPad interface could pair with the sensor and record the temperature anywhere within radio frequency sphere with a 30-meter radius.
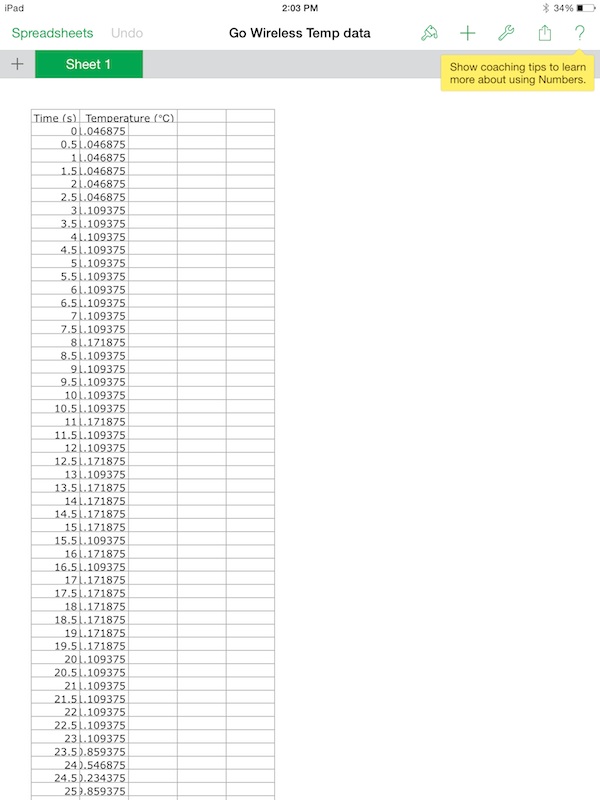
The data from the Go Wireless Temp app can export directly into an iPad spreadsheet app called Numbers. This is a screenshot of the river data, as exported.
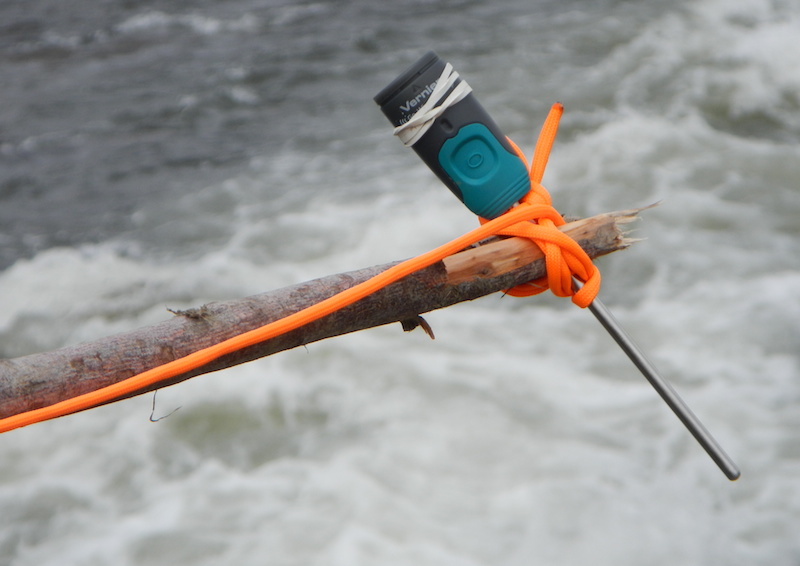
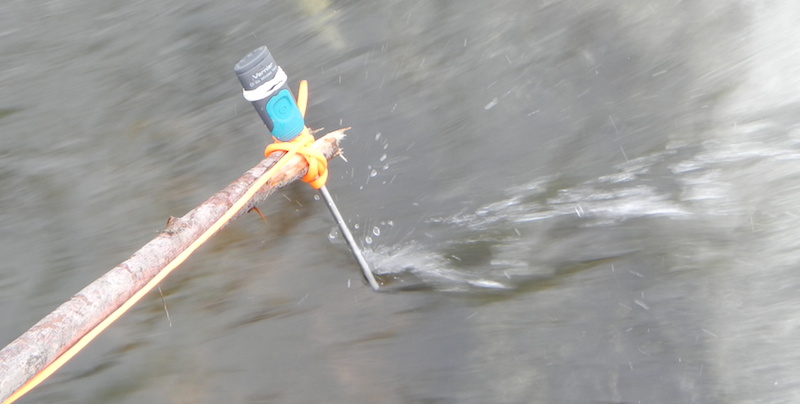
Next, the Go Wireless Temp was tied to a branch so it could be inserted precisely into various water pools. First, it was lowered into a fast-flowing current, then into a nearby still pool, and finally into the water collected inside an old tire.
Based on my tests, it will take at least 10 seconds to get the reading into the ballpark of its final value. The Go Wireless Temp is submersion-rated to 1 meter for 30 minutes.

Using the stick method, the sensor takes the temperature of the tire. It is warmer than the surrounding water.
But the coup de grâce of my afternoon adventures was duct-taping the sensor to a quadcopter drone and flying it. At first, the merits of mounting a sensor with a limited range on something with a much larger range seemed questionable, but the temperature would be recorded as long as the sensor was in range, and the drone wouldn’t fall to the ground when the sensor lost communication.
So, why did I put a Go Wireless Temp on a drone? I guess the easy answer is because I could. But in reality, I saved answering that question until after it was flying. One reason was to measure the temperature radiating off of various roof surfaces, roads, and foliage areas. Another reason was to suspend the probe on a harness, like noted above, and dip it into bodies of water or locations in the water that are normally inaccessible.
One hundred vertical centimeters might be a challenge to fly, but the real issue is the weakened radio strength when the probe is underwater. One solution, which I’ve yet to build, is a personal flotation doughnut, or PFD, for the Go Wireless Temp probe. A small disk of expanded polystyrene (Styrofoam) with the probe poked through the center would allow plenty of slack to build the vertical buffer for safer flight and a much greater margin for error. Stay tuned for that one!
So what would you do with a Go Wireless Temp sensor?
Share your creative ideas in the comments.
Earth Day
By Mary Bigelow
Posted on 2014-03-21
 “Think globally, act locally” is a phrase we hear, and for younger students, thinking locally is important, too. Earth Day is celebrated on April 22, but the activities and investigations described in this month’s featured articles go beyond a single day and encourage students and teachers to consider what happens in their own lives and backyards or neighborhoods.
“Think globally, act locally” is a phrase we hear, and for younger students, thinking locally is important, too. Earth Day is celebrated on April 22, but the activities and investigations described in this month’s featured articles go beyond a single day and encourage students and teachers to consider what happens in their own lives and backyards or neighborhoods.
According to the authors of How Low Can You Go? Interdisciplinary Student-Impact Investigations for Environmental Awareness and Sustainability, students may find it difficult to comprehend global sustainability issues. But younger students can understand local issues and how they affect themselves and their families. In this set of activities, students investigate and analyze their own consumption habits. For example, students study the amount of packaging used in food products, where the ingredients come from, and how food gets from the growers/producers to their homes. An activity on waste generation and landfills has students looking at the trash they produce and how this could be minimized. There are suggestions for other activities on consumer habits, too. [SciLinks: Sustainability, Sustainable Development]
What is the value of live trees versus cutting them down for products we desire? The Value of a Tree: Comparing Carbon Sequestration to Forest Products addresses this question. The students determined their own carbon footprint and calculated how much jet fuel (in the form of biofuel) can be obtained from a tree and compared it to the amount of carbon in the tree if it were left standing. The authors include a pre-post assessment and a student activity sheet, as well as several charts of information and options for alternative activities if the school campus does not include trees. [SciLinks: Forests, Renewable Resources]
Invading the Curriculum: Incorporating Service Learning in the Local Community to Enhance Student Engagement focuses on how the topics of biodiversity and invasive ecology can be combined with service learning to engage students in a local effort. The project was designed to connect the school’s curriculum to local environmental issues. Using a service learning model (described in the article), students and teachers worked with experts in their community to do a biodiversity assessment of their school property and the impact of invasive species. The culminating activity was the design of a native garden. [SciLinks: Invasive Species, Biodiversity]
Are you looking for ways to incorporate engineering activities in science classes? Greenhouse Design: An Engineering Unit lists the components of a good engineering unit. Students were given a challenge to design a greenhouse for a particular region. (The article uses the Northern Territory of Australia, but the authors note that the activity could be modified to use anywhere.) Students researched the abiotic factors in their region and determined which type of plants could be grown. They then developed a design and a budget proposal and built a prototype. The article has photos of these along with a rubric and a unit overview of the time required.
During this time of the year, many classes go outside on field trips. Rather than student doing the ubiquitous scavenger hunt, Get Your Students Outside with Technology describes students created an interpretive trail (even if your school does not have a forested campus, a local park could be used with permission). For points of interest, students described them with text, images, or videos, posting their descriptions in a class Google Map and creating a summary for a trail map. They created QR codes to access the information and made signposts with the codes for users of the trail. The author has many suggestions for making this a do-able project with middle-schoolers.
UV or Not UV? That is a question for your sunglasses takes students beyond wearing sunglasses as fashion statements. In this 5E lesson, students test lenses for their ability to filter UV light using UV-sensitive beads. The article has background information on the history of sunglasses and a student activity sheet. I could see how students would find this interesting at this time of the year. [SciLinks: UV Index, Sun Safety]
 “Think globally, act locally” is a phrase we hear, and for younger students, thinking locally is important, too. Earth Day is celebrated on April 22, but the activities and investigations described in this month’s featured articles go beyond a single day and encourage students and teachers to consider what happens in their own lives and backyards or neighborhoods.
“Think globally, act locally” is a phrase we hear, and for younger students, thinking locally is important, too. Earth Day is celebrated on April 22, but the activities and investigations described in this month’s featured articles go beyond a single day and encourage students and teachers to consider what happens in their own lives and backyards or neighborhoods.
New teacher "nightmare"
By Mary Bigelow
Posted on 2014-03-19
 I am looking forward to my first teaching job, but I’m concerned about how parents will react to my being a “newbie” in the science department. Will this be an issue? What can I do to start off the year on a positive note? My nightmare is that all of the parents will request their children be assigned to a more experienced teacher.
I am looking forward to my first teaching job, but I’m concerned about how parents will react to my being a “newbie” in the science department. Will this be an issue? What can I do to start off the year on a positive note? My nightmare is that all of the parents will request their children be assigned to a more experienced teacher.
—Michael, Richmond, Virginia
First of all, don’t ever apologize for being a first-year teacher. Everyone has to start somewhere, and the fact that you’re concerned means you’re not taking a casual approach to your preparations. Even experienced teachers have nightmares!
I suspect most parents will be very supportive of your efforts. You do have some strong points: you may have new ideas in science instruction and assessment from your college or university teacher training program, you’re probably tech-savvy, and you should be up-to-date on recent science topics in your subject area. It sounds like you’ll be in a secondary situation, so your energy and enthusiasm should connect with students. You don’t have a lot of bad habits to unlearn, either.
Be aware that other adults may play important roles in your students’ lives: guardians, step-parents, grandparents or other relatives, foster parents, and other caregivers. When you use the word “parent” you should consider all of these possibilities.
Communicating with parents early and often is key to developing a positive working relationship. Along with the safety contract you send home at the start of the year, include a course overview and introduce yourself. Focus on your training, background, and other related experiences you had in your field (internships, research projects, volunteer work, or extracurricular activities) that you’ll draw on to relate science to student interests and career goals.
Also let parents know how to contact you through your school email address and phone number (don’t share your personal phone number unless you really want people calling or texting you at all hours!). Be realistic and upfront with parents: “I am teaching from 8:00 until 3:00. I will be glad to return your calls and respond to emails before or after these times.” And then do so promptly.
Take the initiative and contact parents with good news about their child through a postcard, email, or phone call. Share information about an activity the student is doing in class or a project he or she is working on. Some teachers forward photos of the student engaged in a classroom activity (I’d be cautious about having other students identifiable in the photo because of privacy issues). This may sound like a lot of work, but if you do several each day, it becomes part of your routine. You’ll eventually find that you have several templates for this communication that can be customized for each student. Parents appreciate hearing good news! And you’ve opened the door for additional communications.
A class website or blog can also be used to communicate with parents.
Save copies of any written communications you have with parents and document any phone or face-to-face conversations. These notes will be helpful if you do run into a situation with a challenging parent. If you feel that a parent meeting will be confrontational, you can ask your principal, mentor, or another colleague to be present.
Present yourself as a professional in your actions, your appearance, and the way you speak. Find a teacher in your school who has successful relationships with parents and use him or her as a role model.
My recurring nightmare about teaching was showing up on the first day totally unprepared—in a different school with no lesson plans, no materials, no schedule, and no classroom. Fortunately, this dream never came true, but I worked hard to be over–prepared just in case!
For more on working with parents, check out a previous blog on Science and Families. For more on challenges issues facing beginning science teachers, take a look at the NSTA Press book Rise and Shine: A Practical Guide for the Beginning Science Teachers.
Using new technologies
By Mary Bigelow
Posted on 2014-03-14
 Watching children and teenagers use computers, tablets, and smartphones, it’s easy to assume that these digital natives are very familiar with all of the new technologies. I’ve found that while they know what relates to their interests, many students are unaware of the full range of capabilities of their technology as learning tools. As the editor notes, many technological innovations have the potential to transform education. The featured articles in this issue describe some innovative ways teachers and students are using technology in science classrooms.
Watching children and teenagers use computers, tablets, and smartphones, it’s easy to assume that these digital natives are very familiar with all of the new technologies. I’ve found that while they know what relates to their interests, many students are unaware of the full range of capabilities of their technology as learning tools. As the editor notes, many technological innovations have the potential to transform education. The featured articles in this issue describe some innovative ways teachers and students are using technology in science classrooms.
Gathering information used to take a lot of time and effort, but today that information is at our fingertips. So helping students evaluate sources and interpret information becomes more important. And students are no longer limited to sharing information through traditional “reports.” The authors of two articles share their experiences in helping students develop information and media literacy by researching information and creating graphic representations and summaries. They also share resources for creating them.
- Science News Infographics describes how to do a visual read-aloud/think-aloud in which the teacher models how to interpret and question an infographic (the authors include several sources for these, in addition to other news services). The article also describes how to guide students in designing their own infographics, with examples of student projects.
- Using Infographics in the Science Classroom* includes several activities in which students analyze infographics that they find and create their own infographics on class topics. The author notes that students were intrigued by the blending of science, data visiualization, and art into a product that could be easily revised and adapted.
- If you’re looking for topics that could be discusses in infographics, see The Gray Wolf: A Good Case Study or Teens and STDs* in this issue. [SciLinks: Wolf, Wolf Population] [SciLinks: Sexually Transmitted Diseases]
Pinpointing Watershed Pollution on a Virtual Globe* has a 5E lesson that involves students in a study of their local environment. Using Google Earth and other sources, students make predictions, evaluate data, and develop inferences. [SciLinks: Watersheds]
There’s an App for That isn’t just a catchy phrase in advertising. This article is NOT a list of apps to download. The authors describe a project in which students actually designed and produced their own apps based on class topics. It’s not as complicated as it sounds—the article has a list of app design software, a rubric, and a discussion of the value of doing such a project in terms of engineering design and media literacy. What better way to understand apps than to create them yourself!
What if you could transform the traditional written lab report into a product that is engaging for both students and teachers? A New Take on Student Lab Reports describes a study in which the authors investigated the use of screencasts in which students do voice-overs of computer-based data collected during labs. They concluded that “regardless of demonstrated writing ability, students can produce clear, articulate, and careful oral explanations.” There are links to a sample student screencast and screencasting software.
The giant tomes that students carry around (and whose costs keep rising) may be a thing of the past. Textbooks 2.0 discusses digital textbooks such as the new e-Books from NSTA. Digital “textbooks” go beyond static text to include video clips, animations, simulations, online quizzes with feedback, notetaking and highlighting tools, and links to discussion forums.
*Don’t forget to look at the Connections for this issue (March 2014). Even if the article does not quite fit with your lesson agenda, this resource has ideas for handouts, background information sheets, data sheets, rubrics, etc.
 Watching children and teenagers use computers, tablets, and smartphones, it’s easy to assume that these digital natives are very familiar with all of the new technologies. I’ve found that while they know what relates to their interests, many students are unaware of the full range of capabilities of their technology as learning tools. As the editor notes, many technological innovations have the potential to transform education.
Watching children and teenagers use computers, tablets, and smartphones, it’s easy to assume that these digital natives are very familiar with all of the new technologies. I’ve found that while they know what relates to their interests, many students are unaware of the full range of capabilities of their technology as learning tools. As the editor notes, many technological innovations have the potential to transform education.
It's Debatable! Using Socioscientific Issues to Develop Scientific Literacy
By Carole Hayward
Posted on 2014-03-13
“Should schools charge more money for ‘unhealthy’ foods?” “Should animals perform in circuses?” Should rare Earth elements be mined in the United States?” “Should prescription drugs be advertised directly to consumers?”
 In It’s Debatable! Using Socioscientific Issues to Develop Scientific Literacy, authors Dana L. Zeidler and Sami Kahn present a persuasive case for connecting science lessons to real-world questions and issues like these. Seven classroom units give students practice in the research, analysis, and argumentation necessary to grapple with difficult questions and build scientific literacy.
In It’s Debatable! Using Socioscientific Issues to Develop Scientific Literacy, authors Dana L. Zeidler and Sami Kahn present a persuasive case for connecting science lessons to real-world questions and issues like these. Seven classroom units give students practice in the research, analysis, and argumentation necessary to grapple with difficult questions and build scientific literacy.
Today’s students need to be “science literate” in order to contend with these issues, but what exactly does that mean? More than simply knowing the content included in our science standards, our students need to be able to synthesize, analyze, and deliberate over complex socioscientific issues (SSI) which will demand their attention, their input, and perhaps, their vote.
As the authors explain, “As science educators, we do not have a choice but to move our curricula into a new era of contextualized science; our students want to have a say in local and global issues and with their unbridled access to information, they need to be able to identify the positions and motivations of various stakeholders. They also need to be well versed in analyzing the quality of information they receive, including the difference between science and pseudoscience.”
Constructing an SSI unit may seem daunting at first, but the authors suggest that teachers start by adding SSI lessons to already-existing units. For example, if you are doing a unit on the human body, consider incorporating research on a related controversial issue such as, “Should fluoride be added to drinking water?” or “Should fried foods be banned?”
To help facilitate the process, the authors have identified some steps that are useful in guiding teachers through the development and implementation of SSI in their classrooms:
- Identify Topics. Review newspapers, books, internet sources, professional science education-related journals, and television/movies for current issues related to your subject matter and course objectives.
- Collect Resources. Look for a range of sources reflecting a diversity of viewpoints.
- Introduce Topic. Engage students with magazine headlines, articles, advertisements, YouTube videos, photos, models, or other media.
- Prepare Students for Discussions. Set ground rules for class discussions, emphasizing the value of all ideas, mutual respect for participants, and intolerance for mockery or personal attacks.
- Pose Controversial Questions. Introduce contentious questions (e.g., “Should schools charge a ‘fat tax’ for unhealthy foods?”) and challenge “common knowledge” of subject matter (e.g., Are calories from fat different than calories from sugar?”).
- Provide Formal Instruction. Present subject matter in a variety of ways (e.g., direct teaching, laboratory investigations, internet/textbook research, class discussions, guest speakers, field trips, films) to ensure content coverage and student engagement.
- Incorporate Group Activities. Allow students to investigate issues in small groups, emphasizing the analysis of evidence, reinforcement of content matter, monitoring of understanding, consideration of divergent viewpoints, and full participation of all students.
- Provide Guidance in Evaluating Primary and Secondary Sources. Discuss the importance of identifying bias and provide tools for assessing trustworthiness of research sources.
- Assess Knowledge and Reasoning. A variety of “products” that allow students to demonstrate learning can be developed. Assessment should include content understanding as well as its reasoned applications to the issue at hand.
- Have fun! SSI provides opportunities for creativity, engagement, and exploration by students and teachers.
To get a sense of how each lesson in the book is presented and organized, check out the sample chapter: A Need for Speed? Should speed limits be lowered to reduce traffic fatalities? This book is also available an e-book.
“Should schools charge more money for ‘unhealthy’ foods?” “Should animals perform in circuses?” Should rare Earth elements be mined in the United States?” “Should prescription drugs be advertised directly to consumers?”
Breathe new life into your STEM lessons
By Claire Reinburg
Posted on 2014-03-12
Science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) hold tremendous interest for students at all grade levels. The breadth of the topic areas teachers can cover in STEM lessons reinforces for students that these fields are interconnected and linked to exciting scientific and technical developments that are key to our future. The March 2014 issue of NSTA’s Book Beat highlights strong STEM lessons that connect with the Next Generation Science Standards and Common Core State Standards.
Doing Good Science in Middle School, Expanded 2nd Edition: A Practical STEM Guide
Olaf Jorgenson and his coauthors took middle-school science teaching by storm when NSTA Press published the first edition of Doing Good Science in Middle School. Teachers loved the down-to-earth advice and lively lessons in the book and propelled the book to the top of the Science Store bestsellers list. Now the author team has updated and expanded that resource into the just-released Doing Good Science in Middle School, Expanded 2nd Edition: A Practical STEM Guide. This new book offers chapters to help teachers assimilate STEM principles, understand and apply the NGSS and A Framework for K–12 Science Education, and integrate the Common Core literacy and writing standards into science instruction. At the heart of the book are 10 teacher-friendly, ready-to-use STEM activities that connect with NGSS and follow the BSCS 5E model. Lessons highlight key topics in the middle-level curriculum, such as energy transfer (“Keeping Your Cool”), engineering and structural design (“Bridge Buster”), and ecosystems and biological diversity (“Saving the World, One Ecosystem at a Time”). Download the sample chapter “Some Striped Seeds Seem Similar!” for a biology lesson on genetic variation. Students will take on the roles of scientists as they learn about statistics and genetic variation within a species while they focus on discovering statistical patterns that emerge from their data. Check out other exciting NSTA Press STEM books as well: Integrating Engineering and Science in Your Classroom, The Case for STEM Education, and STEM Student Research Handbook.
Special Offer in March 2014
We are offering special savings this month on Science the “Write” Way. This volume gives K–8 teachers a wealth of strategies and lessons focused on writing in science, with articles covering lab reports, science journals, field guides, and interactive science notebooks. Science the “Write” Way is specially priced at $18.17 through March 31, 2014, which is 30% off the regular nonmember price of $25.95. Visit the Science Store to learn more about this book and our newest Spring 2014 books.
Science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) hold tremendous interest for students at all grade levels. The breadth of the topic areas teachers can cover in STEM lessons reinforces for students that these fields are interconnected and linked to exciting scientific and technical developments that are key to our future. The March 2014 issue of NSTA’s Book Beat highlights strong STEM lessons that connect with the Next Generation Science Standards and Common Core State Standards.
NSTA’s K-College Science Education Journals: March 2014 Issues Online
By Lauren Jonas, NSTA Assistant Executive Director
Posted on 2014-03-06
Interactions are our focus this month—in ecosystems and classrooms, among science teachers teaching a variety of disciplines, and using the latest technology. This month’s K-College journals from the National Science Teachers Association have a wealth of articles on how to make the most of the great ideas and possibilities that bubble up via smart collaboration.
 Science and Children
Science and Children
This issue of Science and Children offers engaging ideas, strategies, and resources for helping your students understand how the parts of an ecosystem interact.
Featured articles (please note, only those marked “free” are available to nonmembers with out a fee):
- Free – Editor’s Note: Support for Implementation of NGSS
- Exploring Nature Through a New Lens
- Growing Gardens, Growing Minds
- How Healthy Is Our Pond?
- Free – Our World Without Decomposers: How Scary!
- Outstanding Science Trade Books for Students K–12
- The Amazing Ecology of Terrestrial Isopods
- Full Table of Contents
 Science Scope
Science Scope
Celebrate Earth Day on Tuesday, April 22, 2014, with one or more of the activities found in this issue of Science Scope. We’re sure you’ll find something in this collection that will help focus students’ attention on the world around them and the planet they live on.
Featured articles (please note, only those marked “free” are available to nonmembers without a fee):
- Free – Editor’s Roundtable: Walking a Thin Line
- Get Your Students Outside With Technology
- Greenhouse Design: An Engineering Unit
- Free – How Low Can You Go?: Interdisciplinary Student-Impact Investigations for Environmental Awareness and Sustainability
- Invading the Curriculum: Incorporating Service Learning in the Local Community to Enhance Student Engagement
- Outstanding Science Trade Books for Students K–12
- The Value of a Tree: Comparing Carbon Sequestration to Forest Products
- Full Table of Contents
 The Science Teacher
The Science Teacher
Technology has changed our world. Our classrooms? Not so much. Students spend most of their daily lives interacting with 21st-century technology, but too many classrooms seem stuck in the 19th century, as smartphone and tablet use is often restricted and technology applications are limited. While there are good reasons for schools to be conservative—we don’t want to latch onto the latest gadget of instructional fad—modern technology has the potential to transform education. This edition highlights various ways that teachers are integrating technology into classroom activities, such as designing smartphone apps and colorful infographics, populating Google Earth with data sets, and using screencasts as lab reports. It may well be that we are moving toward a time when tech challenges will not be limited by dollars but only by imagination.
- A New Take on Student Lab Reports
- Free – Editor’s Corner: New Tools—New Possibilities
- Free – Outstanding Science Trade Books for Students K–12
- Pinpointing Watershed Pollution on a Virtual Globe
- Free – Science News Infographics
- There’s An App for That
- Using Infographics in the Science Classroom
- Full Table of Contents
 Journal of College Science Teaching
Journal of College Science Teaching
Read about a new program designed to meet the challenges of educating interdisciplinary scientists by combining mathematics, physics, chemistry, and quantitative thinking with biological applications. The Two-Year Community column describes an initiative in which community college faculty and students partnered with 4-year college colleagues on summer research to cultivate a STEM transfer pathway and expand research capacity at the community college. And in the Research and Teaching section see the article about an unusual method to promote student-centered learning that involved clickers as a mechanism for students to complete in-class quizzes.
Featured articles (please note, only those marked “free” are available to nonmembers without a fee):
- Free – Assessment in Online Learning—It’s a Matter of Time
- Free – Editorial: Good Things
- Examinations That Support Collaborative Learning: The Students’ Perspective
- Explorations in Integrated Science
- Metacognition: An Effective Tool to Promote Success in College Science Learning
- Raising the Bar in Freshman Science Education: Student Lectures, Scientific Papers, and Independent Experiments
- Research and Teaching: Project-Based Instruction With Future STEM Educators: An Interdisciplinary Approach
- Research and Teaching: Student Success Indicators Associated With Clicker-Administered Quizzes in an Honors Introductory Biology Course
- Using the Draw-a-Scientist Test for Inquiry and Evaluation
- Full Table of Contents
Interactions are our focus this month—in ecosystems and classrooms, among science teachers teaching a variety of disciplines, and using the latest technology. This month’s K-College journals from the National Science Teachers Association have a wealth of articles on how to make the most of the great ideas and possibilities that bubble up via smart collaboration.
Ecosystems: Interactions, energy, and dynamics
By Mary Bigelow
Posted on 2014-03-06
 In an NSTA discussion forum, a question was raised about studying ecosystems and food chains at the elementary level. I pointed the readers to articles in this month’s edition of Science & Children, which has a variety of classroom resources and background information for teachers.
In an NSTA discussion forum, a question was raised about studying ecosystems and food chains at the elementary level. I pointed the readers to articles in this month’s edition of Science & Children, which has a variety of classroom resources and background information for teachers.
Many science lessons for young students focus on warm, fuzzy animals. Our World Without Decomposers: How Scary!* describes a series of class activities in which students examine and learn about “bugs, slugs, bacteria, and fungi.” (My middle schoolers would love this, too!) Descriptions of creating a classroom decomposing tank, exploring decomposers a local park, and reflecting on the role these organisms play in an ecosystem are the highlights of this article. [SciLinks: Decomposer, Characteristics of Fungi, Bacteria, Composting, How Does Nature Recycle Materials]
Videos, readings, and classroom activities are good, but nothing beats real outdoor experiences. Ecosystems, Up Close and Personal (The Early Years)* shows how just about any schoolyard can be an ecosystem. When students plant seeds in a school garden or even in a pot, they can begin to understand the relationship between a living thing and the abiotic factors in an ecosystem. A lesson is provided. [SciLinks: How do ecosystems change naturally?, Plant Growth]
Regardless of whether you call them pillbugs or roly-polies, The Amazing Ecology of Terrestrial Isopods* show how these arthropods can be the basis for an engaging study of interactions between organisms and their environment. The authors include a fact sheet on these critters and a description of an outdoor activity in which students observed the organisms and the characteristics of their environment. The students then created an indoor habitat (directions provided) in which they could investigate the behaviors of these low-maintenance classroom animals in more detail. [SciLinks: Arthropods]
Do your students understand that a food chain is more than a diagram of who eats what? If Energy is Neither Created Nor Destroyed, What Happens to It? (Science 101) discusses the energy transfer in an ecosystem. [SciLinks: Food Chains, Food Webs]
Not all evidence and data are numeric. With the prevalence of digital cameras and cell phone cameras, students have an evidence-collecting tool at their fingertips. Exploring Nature Through a New Lens* has suggestions for a student study of the schoolyard habitat. And if you’re thinking about turning part of the school campus into an outdoor learning center, you’ll want to read Ensuring a Safer Outdoor Experience (Safety First)*.[SciLinks: Habitats]
The authors of How Healthy Is Our Pond?* provided students with a real-life scenario for studying the characteristics of a local pond. Students observed the physical and biological surroundings and performed water quality tests for temperature, pH, nitrates, dissolved oxygen, and clarity. The authors describe these tests in detail and include photographs and samples of student data. [SciLinks: Water Quality]
Growing Gardens, Growing Minds* shows how K-4 students went beyond growing seeds in paper cups to designing a community garden at their school. They also learned about nutrition and how plants are part of a healthy diet. The article includes photographs and a grade-by-grade description of class activities related to the project. Seeding Science in Elementary Schools (Methods and Strategies) describes a school-university partnership to establish classroom gardens. [SciLinks: Plants as Food, Plants with Seeds, Seed Germination]
“Adaptation” is a word that can have several meanings, from its everyday one to a more scientific one. Habitat Change: Formative Assessment of a Cautionary Word (Formative Assessment Probes) includes a probe to study students’ perceptions of the process. [SciLinks: Adaptations of Plants, Adaptations of Animals]
Is This Alive? (Science Shorts)* is a question that intrigues students. How do we know? The 5E lesson here focuses on kindergarten students’ explorations of living things and some of their misconceptions. [SciLinks: Living Things]
Let’s Talk Trash (Teaching Through Trade Books)* suggests two trade books on the topic and includes two lessons that help students look at their own choices and how these choices can affect their communities. The 5E lesson Garbage Gurus (K-2) guides students through an analysis of “trash” to determine what might be recyclable. For students in grades 3-5, the 5E lesson Where Does Our Trash Go? examines the trash stream in their community. [SciLinks: Recycling K-4, Recycling 5-8]
*And check out more Connections for this issue (March 2014). Even if the article does not quite fit with your lesson agenda, there are ideas and links for handouts, background information pages, data sheets, rubrics, and other resources.
 In an NSTA discussion forum, a question was raised about studying ecosystems and food chains at the elementary level. I pointed the readers to articles in this month’s edition of Science & Children, which has a variety of classroom resources and background information for teachers.
In an NSTA discussion forum, a question was raised about studying ecosystems and food chains at the elementary level. I pointed the readers to articles in this month’s edition of Science & Children, which has a variety of classroom resources and background information for teachers.
Ecosystems outside the school door
By Peggy Ashbrook
Posted on 2014-03-06
 Since it is now March and in my area we just had our 10th snow day, I am dreaming of planting seeds rather than actually planting them. What should the children plant in the raised bed school garden, a tiny sliver of ground that could not be incorporated into the play area because there is a telephone pole in the way? The children offer very general ideas: “flowers,” “carrots,” and “peas” (from the older children who remember them from last spring). These are great ideas and we can do them all—first peas, and later carrots and flowers, all in small amounts. There are wonderful children’s fiction and non-fiction books and songs about gardening with children. Post your favorites in the comments below.
Since it is now March and in my area we just had our 10th snow day, I am dreaming of planting seeds rather than actually planting them. What should the children plant in the raised bed school garden, a tiny sliver of ground that could not be incorporated into the play area because there is a telephone pole in the way? The children offer very general ideas: “flowers,” “carrots,” and “peas” (from the older children who remember them from last spring). These are great ideas and we can do them all—first peas, and later carrots and flowers, all in small amounts. There are wonderful children’s fiction and non-fiction books and songs about gardening with children. Post your favorites in the comments below.
Like many schools, we don’t have a windowsill with full sun where we can grow healthy seedlings inside. We do sprout seeds in plastic bags, clear containers and on sponges, to see the delicate roots and sprouts grow. But growing a plant to maturity must wait until we can plant in the ground, currently under a blanket of snow.
I’m also interested in having plants that will attract butterflies because they are so pretty and the children are attracted by their colors and motion. Children do like to find ants, roly-polies, slugs and earthworm, and spot bees, too. These observations add up over time to a beginning understanding of the ecosystem, and how the small animals fit into it. The ants are often found in groups, worms are always found in or on the ground, the roly-polies and slugs are most abundant in damp places, and the bees are focused on flowers. This concept, of each animal meeting its needs within an ecosystem, is more apparent in butterflies because their needs change with change in life stage after they come from the egg as larva, change to pupa, and then to adult.
 In the March 2014 Early Years column in Science and Children, I wrote about observing the growth of a fennel plant (Foeniculum vulgare) and the animals that use it, over time. In the school yard, we have a fennel plant whose leaves are food for the larvae (caterpillars) of Black Swallowtail butterflies. The adult butterfly does drink nectar from the flowers but seems to prefer the nectar of annual flowering plants. By planting another favorite Black Swallowtail larval food, parsley, nearby, we can almost guarantee that we will be able to find these caterpillars. These caterpillars are safe to touch—gently, for the caterpillar’s sake. Research the species of butterflies that live in your area to learn which are safe for children to touch and which have stinging hairs. Some species should not be disturbed because they are an endangered species. The common and not-endangered butterfly species in your region may not be the same species as the ones I have my children observe as the spring season progresses.
In the March 2014 Early Years column in Science and Children, I wrote about observing the growth of a fennel plant (Foeniculum vulgare) and the animals that use it, over time. In the school yard, we have a fennel plant whose leaves are food for the larvae (caterpillars) of Black Swallowtail butterflies. The adult butterfly does drink nectar from the flowers but seems to prefer the nectar of annual flowering plants. By planting another favorite Black Swallowtail larval food, parsley, nearby, we can almost guarantee that we will be able to find these caterpillars. These caterpillars are safe to touch—gently, for the caterpillar’s sake. Research the species of butterflies that live in your area to learn which are safe for children to touch and which have stinging hairs. Some species should not be disturbed because they are an endangered species. The common and not-endangered butterfly species in your region may not be the same species as the ones I have my children observe as the spring season progresses.
 Resources that might be of use include online catalogues maintained by volunteers, online and in print information sheets from government agricultural services, and identification books such as the Peterson First Guide to Caterpillars of North America by Amy Wright. I like this book because it describes 120 common species and shows the caterpillars, their adult forms and many of their host plants.
Resources that might be of use include online catalogues maintained by volunteers, online and in print information sheets from government agricultural services, and identification books such as the Peterson First Guide to Caterpillars of North America by Amy Wright. I like this book because it describes 120 common species and shows the caterpillars, their adult forms and many of their host plants.
Did you know that digital versions of NSTA journals are available for members to read on your computer as well as your Kindle Fire, Android tablet/phone, or iPad/iPhone?
 Since it is now March and in my area we just had our 10th snow day, I am dreaming of planting seeds rather than actually planting them. What should the children plant in the raised bed school garden, a tiny sliver of ground that could not be incorporated into the play area because there is a telephone pole in the way?
Since it is now March and in my area we just had our 10th snow day, I am dreaming of planting seeds rather than actually planting them. What should the children plant in the raised bed school garden, a tiny sliver of ground that could not be incorporated into the play area because there is a telephone pole in the way?
Sylvia Shugrue Award winner 2013
By admin
Posted on 2014-03-05
 As Director of Distance Learning for University of Minnesota’s Bell Museum of Natural history, each year Chris Tower created and provided professional development for more than 300 teachers throughout Minnesota and Wisconsin via two distance–learning, cross-curricular science programs: the JASON Project and BellLive.
As Director of Distance Learning for University of Minnesota’s Bell Museum of Natural history, each year Chris Tower created and provided professional development for more than 300 teachers throughout Minnesota and Wisconsin via two distance–learning, cross-curricular science programs: the JASON Project and BellLive.
In his current position, he has established a service-learning water quality study for fourth grade; designed and collaborated with students, teachers, parents, the administration, the city, and businesses to create a rain garden and a community produce garden; presented garden programs to other districts’ teachers, parents, and community members; worked on district-level science review teams and wrote science curriculum for upper-elementary levels; and wrote STEM curriculum for Minnesota’s Department of Education. A school technology leader, he produces a live school wide newscast with students.
“His creativity and willingness to experiment and explore new opportunities energizes our community,” says his principal. His district’s elementary curriculum coordinator describes him as “a real champion of both science and service learning” who “enhances the traditional science curriculum by making meaningful connections for students, while asking them for ways to give back to the community.”
Tower’s winning lesson, The Community Garden Environment Lesson Plan, is aimed at 4th and 5th grade students. The interdisciplinary lesson includes connections to science, literacy, and math, and includes essential elements of Service-Learning. This lesson addresses the Minnesota Science Standards related to environments, living systems, and inquiry.
 As Director of Distance Learning for University of Minnesota’s Bell Museum of Natural history, each year Chris Tower created and provided professional development for more than 300 teachers throughout Minnesota and Wisconsin via two distance–learning, cross-curricular science programs: the JASON Project and BellLive.
As Director of Distance Learning for University of Minnesota’s Bell Museum of Natural history, each year Chris Tower created and provided professional development for more than 300 teachers throughout Minnesota and Wisconsin via two distance–learning, cross-curricular science programs: the JASON Project and BellLive.










